外部接口¶
Odoo 通常通过模块进行内部扩展,但其许多功能以及所有数据也对外部开放,可用于外部分析或与各种工具集成。模型 API 的一部分可通过 XML-RPC 轻松访问,并且可以从多种编程语言中使用。
重要
从 PHP 8 开始,XML-RPC 扩展可能默认不可用。请查看 手册 以获取安装步骤。
注解
通过外部 API 访问数据仅在 自定义 Odoo 定价计划中可用。One App Free 或 标准 计划不提供外部 API 的访问权限。如需更多信息,请访问 Odoo 定价页面 或联系您的客户成功经理。
另请参见
连接¶
配置¶
如果你已经安装了 Odoo 服务器,可以直接使用它的参数。
重要
对于 Odoo Online 实例(<domain>.odoo.com),用户不会设置 本地 密码(因为您是通过 Odoo Online 认证系统登录的,而不是通过实例本身)。要在 Odoo Online 实例上使用 XML-RPC,您需要在要使用的用户账户上设置密码:
使用管理员账户登录您的实例。
转到:menuselection:
设置 --> 用户与公司 --> 用户。点击您用于 XML-RPC 访问的用户。
单击 动作 并选择 更改密码。
设置 新密码 值,然后点击 更改密码。
服务器网址 是实例的域名(例如 https://mycompany.odoo.com),数据库名称 是实例的名称(例如 mycompany)。用户名 是配置的用户的登录名,如 更改密码 屏幕上所示。
url = <insert server URL>
db = <insert database name>
username = 'admin'
password = <insert password for your admin user (default: admin)>
url = <insert server URL>
db = <insert database name>
username = "admin"
password = <insert password for your admin user (default: admin)>
$url = <insert server URL>;
$db = <insert database name>;
$username = "admin";
$password = <insert password for your admin user (default: admin)>;
final String url = <insert server URL>,
db = <insert database name>,
username = "admin",
password = <insert password for your admin user (default: admin)>;
var (
url = <insert server URL>
db = <insert database name>
username = "admin"
password = <insert password for your admin user (default: admin)>
)
API 密钥¶
14.0 新版功能.
Odoo 支持 API 密钥,并且(根据模块或设置)可能在执行 Web 服务操作时 需要 这些密钥。
使用 API 密钥的方式是将脚本中的 密码 替换为密钥。登录名仍然有效。您应像保存密码一样谨慎地存储 API 密钥,因为它们本质上为您的用户账户提供了相同的访问权限(尽管它们不能通过界面进行登录)。
为了将密钥添加到您的账户,请转到您的 首选项`(或 :guilabel:`我的资料):
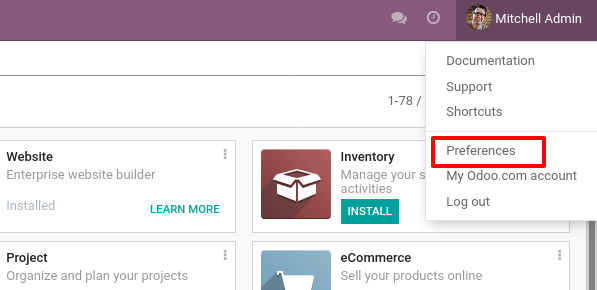
然后打开 账户安全 选项卡,并点击 新建 API 密钥:
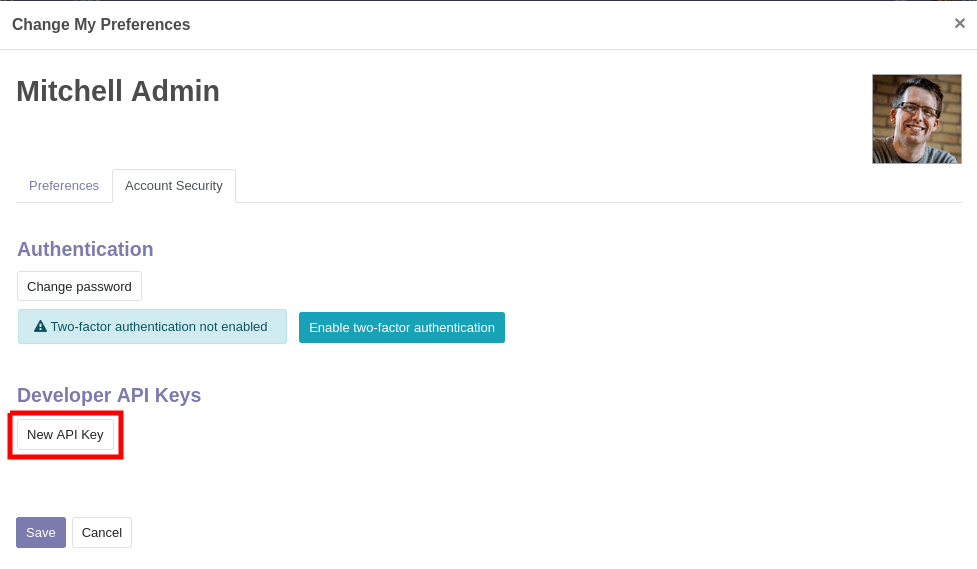
输入密钥的描述,此描述应尽可能清晰和完整:这是你以后识别自己的密钥并判断是否应该删除它们或保留它们的唯一方式。
点击 生成密钥,然后复制提供的密钥。请妥善保存此密钥:它相当于您的密码,就像您的密码一样,系统之后将无法检索或再次显示该密钥。如果您丢失了此密钥,您将不得不创建一个新的密钥(并且可能需要删除已丢失的密钥)。
一旦你在账户中配置了密钥,它们将显示在 新建 API 密钥 按钮上方,并且你可以删除它们:
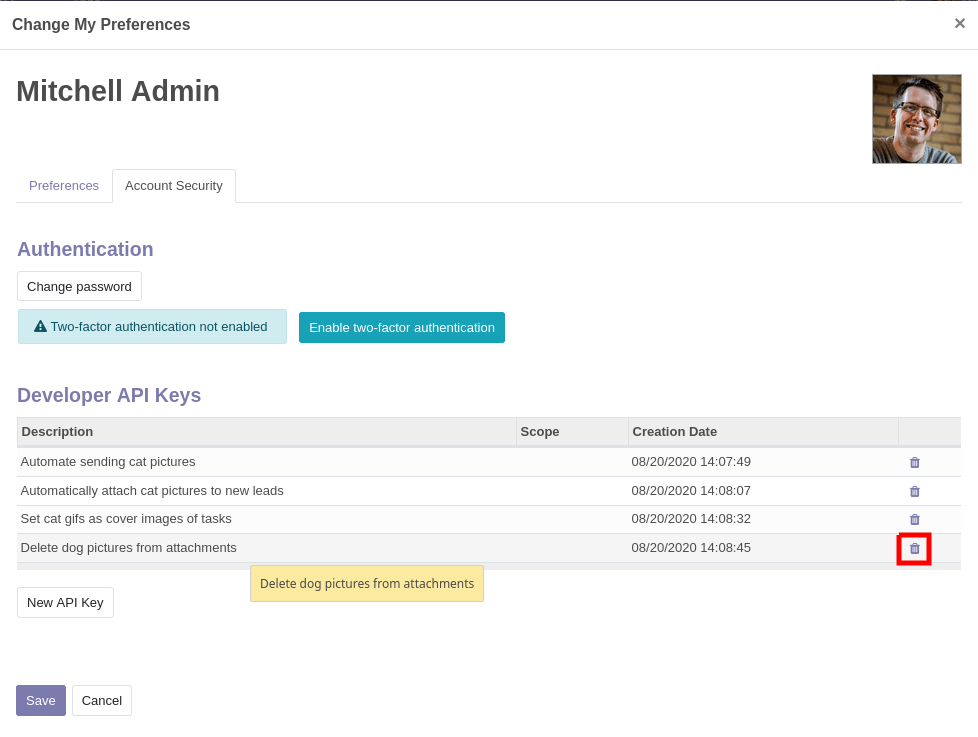
已删除的接口密钥无法恢复或重新设置。您需要生成一个新的密钥,并更新所有使用旧密钥的位置。
测试数据库¶
要使探索更加简便,您也可以通过 https://demo.odoo.com 请求一个测试数据库:
import xmlrpc.client
info = xmlrpc.client.ServerProxy('https://demo.odoo.com/start').start()
url, db, username, password = info['host'], info['database'], info['user'], info['password']
require "xmlrpc/client"
info = XMLRPC::Client.new2('https://demo.odoo.com/start').call('start')
url, db, username, password = info['host'], info['database'], info['user'], info['password']
require_once('ripcord.php');
$info = ripcord::client('https://demo.odoo.com/start')->start();
list($url, $db, $username, $password) = array($info['host'], $info['database'], $info['user'], $info['password']);
注解
这些示例使用了 Ripcord 库,该库提供了一个简单的 XML-RPC 接口。Ripcord 要求在您的 PHP 安装中启用 XML-RPC 支持。
由于调用是通过 HTTPS 进行的,因此还需要启用 OpenSSL 扩展。
final XmlRpcClient client = new XmlRpcClient();
final XmlRpcClientConfigImpl start_config = new XmlRpcClientConfigImpl();
start_config.setServerURL(new URL("https://demo.odoo.com/start"));
final Map<String, String> info = (Map<String, String>)client.execute(
start_config, "start", emptyList());
final String url = info.get("host"),
db = info.get("database"),
username = info.get("user"),
password = info.get("password");
client, err := xmlrpc.NewClient("https://demo.odoo.com/start", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
info := map[string]string{}
client.Call("start", nil, &info)
url = info["host"].(string)
db = info["database"].(string)
username = info["user"].(string)
password = info["password"].(string)
登录¶
Odoo 要求 API 的使用者在查询大部分数据之前必须进行身份验证。
xmlrpc/2/common 端点提供不需要身份验证的元调用,例如身份验证本身或获取版本信息。在尝试进行身份验证之前,验证连接信息是否正确的最简单调用是请求服务器的版本。身份验证本身通过 authenticate 函数完成,并返回一个用户标识符(uid),该标识符用于已身份验证的调用中,而不是登录名。
common = xmlrpc.client.ServerProxy('{}/xmlrpc/2/common'.format(url))
common.version()
common = XMLRPC::Client.new2("#{url}/xmlrpc/2/common")
common.call('version')
$common = ripcord::client("$url/xmlrpc/2/common");
$common->version();
final XmlRpcClientConfigImpl common_config = new XmlRpcClientConfigImpl();
common_config.setServerURL(new URL(String.format("%s/xmlrpc/2/common", url)));
client.execute(common_config, "version", emptyList());
client, err := xmlrpc.NewClient(fmt.Sprintf("%s/xmlrpc/2/common", url), nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
common := map[string]any{}
if err := client.Call("version", nil, &common); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
{
"server_version": "13.0",
"server_version_info": [13, 0, 0, "final", 0],
"server_serie": "13.0",
"protocol_version": 1,
}
uid = common.authenticate(db, username, password, {})
uid = common.call('authenticate', db, username, password, {})
$uid = $common->authenticate($db, $username, $password, array());
int uid = (int)client.execute(common_config, "authenticate", asList(db, username, password, emptyMap()));
var uid int64
if err := client.Call("authenticate", []any{
db, username, password,
map[string]any{},
}, &uid); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
调用方法¶
第二个端点是 xmlrpc/2/object。它用于通过 execute_kw RPC 函数调用 Odoo 模型的电话。
每次对 execute_kw 的调用包含以下参数:
要使用的数据库,字符串
用户的 ID(通过
authenticate获取),一个整数用户的密码,一个字符串
模型名称,一个字符串
方法名称,字符串
按位置传递的参数数组/列表
一个通过关键词传递的参数映射/字典(可选)
Example
例如,要在 res.partner 模型中搜索记录,我们可以调用 name_search,并将 name 通过位置参数传递,将 limit 通过关键字参数传递(以获取最多 10 条结果):
models = xmlrpc.client.ServerProxy('{}/xmlrpc/2/object'.format(url))
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'name_search', ['foo'], {'limit': 10})
models = XMLRPC::Client.new2("#{url}/xmlrpc/2/object").proxy
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'name_search', ['foo'], {limit: 10})
$models = ripcord::client("$url/xmlrpc/2/object");
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'name_search', array('foo'), array('limit' => 10));
final XmlRpcClient models = new XmlRpcClient() {{
setConfig(new XmlRpcClientConfigImpl() {{
setServerURL(new URL(String.format("%s/xmlrpc/2/object", url)));
}});
}};
models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "name_search",
asList("foo"),
new HashMap() {{ put("limit", 10); }}
));
models, err := xmlrpc.NewClient(fmt.Sprintf("%s/xmlrpc/2/object", url), nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var result bool
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "name_search",
[]string{"foo"},
map[string]bool{"limit": 10},
}, &result); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
true
列出记录¶
记录可以通过 search() 进行列出和过滤。
search() 接受一个必填的 :ref:`筛选器 <reference/orm/domains>`(可能为空),并返回所有符合筛选器条件的记录的数据库标识符。
Example
要列出客户公司,例如:
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', true]]])
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'search', array(array(array('is_company', '=', true))));
asList((Object[])models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
asList(asList(
asList("is_company", "=", true)))
)));
var records []int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
[]any{[]any{
[]any{"is_company", "=", true},
}},
}, &records); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[7, 18, 12, 14, 17, 19, 8, 31, 26, 16, 13, 20, 30, 22, 29, 15, 23, 28, 74]
分页¶
默认情况下,搜索将返回所有符合条件的记录的 ID,这可能是一个很大的数字。可以使用 offset 和 limit 参数来仅检索所有匹配记录中的一部分。
Example
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'offset': 10, 'limit': 5})
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', true]]], {offset: 10, limit: 5})
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'search', array(array(array('is_company', '=', true))), array('offset'=>10, 'limit'=>5));
asList((Object[])models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
asList(asList(
asList("is_company", "=", true))),
new HashMap() {{ put("offset", 10); put("limit", 5); }}
)));
var records []int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
[]any{[]any{
[]any{"is_company", "=", true},
}},
map[string]int64{"offset": 10, "limit": 5},
}, &records); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[13, 20, 30, 22, 29]
统计记录¶
与其检索可能非常庞大的记录列表并进行计数,可以使用 search_count() 来仅获取匹配查询的记录数量。它接受与 search() 相同的 领域 筛选器,且不接受其他参数。
Example
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search_count', [[['is_company', '=', True]]])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search_count', [[['is_company', '=', true]]])
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'search_count', array(array(array('is_company', '=', true))));
(Integer)models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search_count",
asList(asList(
asList("is_company", "=", true)))
));
var counter int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search_count",
[]any{[]any{
[]any{"is_company", "=", true},
}},
}, &counter); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
19
注解
调用 search 然后 ``search_count``(或反过来)可能在其他用户使用服务器时无法得到一致的结果:因为在两次调用之间,存储的数据可能已经发生了变化。
读取记录¶
记录数据可通过 read() 方法访问,该方法接收一个 ID 列表(如 search() 返回的列表),并可选地接收一个要获取的字段列表。默认情况下,它会获取当前用户可以读取的所有字段,这通常是一个很大的数量。
Example
ids = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'limit': 1})
[record] = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'read', [ids])
# count the number of fields fetched by default
len(record)
ids = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['is_company', '=', true]]], {limit: 1})
record = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'read', [ids]).first
# count the number of fields fetched by default
record.length
$ids = $models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'search', array(array(array('is_company', '=', true))), array('limit'=>1));
$records = $models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'read', array($ids));
// count the number of fields fetched by default
count($records[0]);
final List ids = asList((Object[])models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
asList(asList(
asList("is_company", "=", true))),
new HashMap() {{ put("limit", 1); }})));
final Map record = (Map)((Object[])models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "read",
asList(ids)
)
))[0];
// count the number of fields fetched by default
record.size();
var ids []int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
[]any{[]any{
[]any{"is_company", "=", true},
}},
map[string]int64{"limit": 1},
}, &ids); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var records []any
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "read",
ids,
}, &records); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// count the number of fields fetched by default
count := len(records)
结果:
121
相反,仅拣货三个被认为有趣的字段。
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'read', [ids], {'fields': ['name', 'country_id', 'comment']})
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'read', [ids], {fields: %w(name country_id comment)})
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'read', array($ids), array('fields'=>array('name', 'country_id', 'comment')));
asList((Object[])models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "read",
asList(ids),
new HashMap() {{
put("fields", asList("name", "country_id", "comment"));
}}
)));
var recordFields []map[string]any
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "read",
ids,
map[string][]string{
"fields": {"name", "country_id", "comment"},
},
}, &recordFields); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[{"comment": false, "country_id": [21, "Belgium"], "id": 7, "name": "Agrolait"}]
注解
即使未请求 id 字段,它始终会被返回。
列出记录字段¶
fields_get() 可用于检查模型的字段,并查看哪些字段似乎值得关注。
由于它会返回大量元数据(它也被客户端程序使用),在打印之前应该进行过滤,对人类用户最有用的条目包括 ``string``(字段的标签)、``help``(如果有的话的帮助文本)和 ``type``(以了解预期的值,或在更新记录时发送的值)。
Example
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'fields_get', [], {'attributes': ['string', 'help', 'type']})
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'fields_get', [], {attributes: %w(string help type)})
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'fields_get', array(), array('attributes' => array('string', 'help', 'type')));
(Map<String, Map<String, Object>>)models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "fields_get",
emptyList(),
new HashMap() {{
put("attributes", asList("string", "help", "type"));
}}
));
recordFields := map[string]string{}
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "fields_get",
[]any{},
map[string][]string{
"attributes": {"string", "help", "type"},
},
}, &recordFields); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
{
"ean13": {
"type": "char",
"help": "BarCode",
"string": "EAN13"
},
"property_account_position_id": {
"type": "many2one",
"help": "The fiscal position will determine taxes and accounts used for the partner.",
"string": "Fiscal Position"
},
"signup_valid": {
"type": "boolean",
"help": "",
"string": "Signup Token is Valid"
},
"date_localization": {
"type": "date",
"help": "",
"string": "Geo Localization Date"
},
"ref_company_ids": {
"type": "one2many",
"help": "",
"string": "Companies that refers to partner"
},
"sale_order_count": {
"type": "integer",
"help": "",
"string": "# of Sales Order"
},
"purchase_order_count": {
"type": "integer",
"help": "",
"string": "# of Purchase Order"
},
搜索和读取¶
由于这是一个非常常见的任务,Odoo 提供了 search_read() 的快捷方法,正如其名称所示,该方法等同于先执行 search() 再执行 read(),但可以避免执行两次请求并保留 ID。
它的参数与 search() 类似,但还可以接受一个 fields 列表(如 read() 所示,如果未提供该列表,则会获取匹配记录的所有字段)。
Example
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search_read', [[['is_company', '=', True]]], {'fields': ['name', 'country_id', 'comment'], 'limit': 5})
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search_read', [[['is_company', '=', true]]], {fields: %w(name country_id comment), limit: 5})
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'search_read', array(array(array('is_company', '=', true))), array('fields'=>array('name', 'country_id', 'comment'), 'limit'=>5));
asList((Object[])models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search_read",
asList(asList(
asList("is_company", "=", true))),
new HashMap() {{
put("fields", asList("name", "country_id", "comment"));
put("limit", 5);
}}
)));
var recordFields []map[string]any
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search_read",
[]any{[]any{
[]any{"is_company", "=", true},
}},
map[string]any{
"fields": []string{"name", "country_id", "comment"},
"limit": 5,
},
}, &recordFields); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[
{
"comment": false,
"country_id": [ 21, "Belgium" ],
"id": 7,
"name": "Agrolait"
},
{
"comment": false,
"country_id": [ 76, "France" ],
"id": 18,
"name": "Axelor"
},
{
"comment": false,
"country_id": [ 233, "United Kingdom" ],
"id": 12,
"name": "Bank Wealthy and sons"
},
{
"comment": false,
"country_id": [ 105, "India" ],
"id": 14,
"name": "Best Designers"
},
{
"comment": false,
"country_id": [ 76, "France" ],
"id": 17,
"name": "Camptocamp"
}
]
创建记录¶
使用 create() 可以创建模型的记录。该方法创建一条记录并返回其数据库标识符。
create() 接受一个字段到值的映射,用于初始化记录。对于任何具有默认值且未通过映射参数设置的字段,将使用默认值。
Example
id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'create', [{'name': "New Partner"}])
id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'create', [{name: "New Partner"}])
$id = $models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'create', array(array('name'=>"New Partner")));
final Integer id = (Integer)models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "create",
asList(new HashMap() {{ put("name", "New Partner"); }})
));
var id int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "create",
[]map[string]string{
{"name": "New Partner"},
},
}, &id); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
78
更新记录¶
可以使用 write() 更新记录。它接受要更新的记录列表以及一个包含更新字段和值的映射,类似于 create()。
可以同时更新多条记录,但它们在被设置的字段上将获得相同的值。无法执行“计算”更新(即要设置的值依赖于记录的现有值的情况)。
Example
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'write', [[id], {'name': "Newer partner"}])
# get record name after having changed it
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'read', [[id], ['display_name']])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'write', [[id], {name: "Newer partner"}])
# get record name after having changed it
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'read', [[id], ['display_name']])
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'write', array(array($id), array('name'=>"Newer partner")));
// get record name after having changed it
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password,
'res.partner', 'read', array(array($id), array('display_name')));
models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "write",
asList(
asList(id),
new HashMap() {{ put("name", "Newer Partner"); }}
)
));
// get record name after having changed it
asList((Object[])models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "read",
asList(asList(id), asList("display_name"))
)));
var result bool
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "write",
[]any{
[]int64{id},
map[string]string{"name": "Newer partner"},
},
}, &result); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// get record name after having changed it
var record []any
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "name_get",
[]any{
[]int64{id},
},
}, &record); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[[78, "Newer partner"]]
删除记录¶
可以通过将它们的 ID 传递给 unlink() 方法来批量删除记录。
Example
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'unlink', [[id]])
# check if the deleted record is still in the database
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['id', '=', id]]])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'unlink', [[id]])
# check if the deleted record is still in the database
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'res.partner', 'search', [[['id', '=', id]]])
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'unlink', array(array($id)));
// check if the deleted record is still in the database
$models->execute_kw(
$db, $uid, $password, 'res.partner', 'search', array(array(array('id', '=', $id)))
);
models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "unlink",
asList(asList(id))));
// check if the deleted record is still in the database
asList((Object[])models.execute("execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
asList(asList(asList("id", "=", 78)))
)));
var result bool
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "unlink",
[]any{
[]int64{id},
},
}, &result); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// check if the deleted record is still in the database
var record []any
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"res.partner", "search",
[]any{[]any{
[]any{"id", "=", id},
}},
}, &record); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[]
检查与内省¶
虽然我们之前使用 fields_get() 来查询模型,并且从一开始就在使用任意模型,但 Odoo 将大多数模型的元数据存储在几个元模型中,这些元模型允许通过 XML-RPC 实时查询系统并修改模型和字段(尽管有一些限制)。
模型¶
通过其各个字段,提供有关 Odoo 模型的信息。
名称该模型的可读描述
模型系统中每个模型的名称
状态是否通过 Python 代码(
base)生成的模型,或是通过创建ir.model记录(manual)生成的模型字段ID视图ID访问权限One2many关系指向模型上设置的 引用/安全/访问控制列表。
ir.model 可用于
查询系统中已安装的模型(作为对模型进行操作的前提条件,或用于探索系统的相关内容)。
获取有关特定模型的信息(通常是列出与之相关的字段)。
通过 RPC 动态创建新模型。
重要
自定义模型名称必须以
x_开头。state必须提供并设置为manual,否则模型将不会被加载。无法向自定义模型中添加新的 方法,只能添加字段。
Example
一个自定义模型最初将仅包含所有模型上可用的“内置”字段:
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'ir.model', 'create', [{
'name': "Custom Model",
'model': "x_custom_model",
'state': 'manual',
}])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'x_custom_model', 'fields_get', [], {'attributes': ['string', 'help', 'type']})
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'ir.model', 'create', array(array(
'name' => "Custom Model",
'model' => 'x_custom_model',
'state' => 'manual'
)));
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'x_custom_model', 'fields_get', array(), array('attributes' => array('string', 'help', 'type')));
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'ir.model', 'create', [{
name: "Custom Model",
model: 'x_custom_model',
state: 'manual'
}])
fields = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'x_custom_model', 'fields_get', [], {attributes: %w(string help type)})
models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"ir.model", "create",
asList(new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("name", "Custom Model");
put("model", "x_custom_model");
put("state", "manual");
}})
));
final Object fields = models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"x_custom_model", "fields_get",
emptyList(),
new HashMap<String, Object> () {{
put("attributes", asList(
"string",
"help",
"type"));
}}
));
var id int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"ir.model", "create",
[]map[string]string{
{
"name": "Custom Model",
"model": "x_custom_model",
"state": "manual",
},
},
}, &id); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
recordFields := map[string]string{}
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"x_custom_model", "fields_get",
[]any{},
map[string][]string{
"attributes": {"string", "help", "type"},
},
}, &recordFields); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
{
"create_uid": {
"type": "many2one",
"string": "Created by"
},
"create_date": {
"type": "datetime",
"string": "Created on"
},
"__last_update": {
"type": "datetime",
"string": "Last Modified on"
},
"write_uid": {
"type": "many2one",
"string": "Last Updated by"
},
"write_date": {
"type": "datetime",
"string": "Last Updated on"
},
"display_name": {
"type": "char",
"string": "Display Name"
},
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"string": "Id"
}
}
模型.字段¶
提供有关 Odoo 模型字段的信息,并允许在不使用 Python 代码的情况下添加自定义字段。
模型ID名称字段的技术名称(在
read或write中使用)字段描述该字段的用户可读标签(例如
fields_get中的string)类型字段的 类型
状态该字段是通过 Python 代码(
base)创建的,还是通过ir.model.fields``(``manual)手动创建的。required,readonly,translate启用字段上的相应标志
组选择,大小,on_delete,关系,关系字段,域特定类型的属性和自定义设置,请参阅 字段文档 以获取详细信息
重要
与自定义模型类似,只有使用
state="manual"创建的新字段才会在模型上被激活为实际字段。计算字段不能通过
ir.model.fields添加,某些字段元数据(默认值、onchange)也无法设置。
Example
id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'ir.model', 'create', [{
'name': "Custom Model",
'model': "x_custom",
'state': 'manual',
}])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'ir.model.fields', 'create', [{
'model_id': id,
'name': 'x_name',
'ttype': 'char',
'state': 'manual',
'required': True,
}])
record_id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'x_custom', 'create', [{'x_name': "test record"}])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'x_custom', 'read', [[record_id]])
$id = $models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'ir.model', 'create', array(array(
'name' => "Custom Model",
'model' => 'x_custom',
'state' => 'manual'
)));
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'ir.model.fields', 'create', array(array(
'model_id' => $id,
'name' => 'x_name',
'ttype' => 'char',
'state' => 'manual',
'required' => true
)));
$record_id = $models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'x_custom', 'create', array(array('x_name' => "test record")));
$models->execute_kw($db, $uid, $password, 'x_custom', 'read', array(array($record_id)));
id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'ir.model', 'create', [{
name: "Custom Model",
model: "x_custom",
state: 'manual'
}])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'ir.model.fields', 'create', [{
model_id: id,
name: "x_name",
ttype: "char",
state: "manual",
required: true
}])
record_id = models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'x_custom', 'create', [{x_name: "test record"}])
models.execute_kw(db, uid, password, 'x_custom', 'read', [[record_id]])
final Integer id = (Integer)models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"ir.model", "create",
asList(new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("name", "Custom Model");
put("model", "x_custom");
put("state", "manual");
}})
));
models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"ir.model.fields", "create",
asList(new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("model_id", id);
put("name", "x_name");
put("ttype", "char");
put("state", "manual");
put("required", true);
}})
));
final Integer record_id = (Integer)models.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"x_custom", "create",
asList(new HashMap<String, Object>() {{
put("x_name", "test record");
}})
));
client.execute(
"execute_kw", asList(
db, uid, password,
"x_custom", "read",
asList(asList(record_id))
));
var id int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"ir.model", "create",
[]map[string]string{
{
"name": "Custom Model",
"model": "x_custom",
"state": "manual",
},
},
}, &id); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var fieldId int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"ir.model.fields", "create",
[]map[string]any{
{
"model_id": id,
"name": "x_name",
"ttype": "char",
"state": "manual",
"required": true,
},
},
}, &fieldId); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var recordId int64
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"x_custom", "create",
[]map[string]string{
{"x_name": "test record"},
},
}, &recordId); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
var recordFields []map[string]any
if err := models.Call("execute_kw", []any{
db, uid, password,
"x_custom", "read",
[][]int64{{recordId}},
}, recordFields); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
结果:
[
{
"create_uid": [1, "Administrator"],
"x_name": "test record",
"__last_update": "2014-11-12 16:32:13",
"write_uid": [1, "Administrator"],
"write_date": "2014-11-12 16:32:13",
"create_date": "2014-11-12 16:32:13",
"id": 1,
"display_name": "test record"
}
]